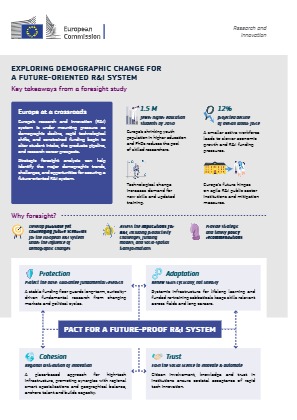
What lies ahead for universities? A new futures research study from the University of Turku maps multiple pathways and tensions that could transform how universities teach, research, and serve society.
Introduction
Researchers of the University of Turku have published a comprehensive report "Future directions and possibilities for the university: Report on literature review and Delphi study" (Virmajoki et al. 2024) about the possible future trajectories of the university of Turku. The report, which is uploaded here and also available on utupub.fi, is part of a larger project - Strategic Foresight and Futures Thinking Initiative.
The report, conducted by the Strategic Planning Unit of the University of Turku together with Finland Futures Research Centre (FFRC), contains the results of the analysis of the operating environment of universities. Operating environment here refers to the broader context of trends, challenges, and conditions - both nationally and globally - that affect how universities function and perform their core activities in teaching and research. While the report has as its scope the University of Turku, its findings and especially the approach are more broadly relevant, particularly in Europe.
Analysis of Operating Environment as Research
The analysis of the operating environment was primarily based on a literature review and a subsequent Delphi survey. We reviewed over 200 scientific texts relevant to the subject. It quickly became evident how multifaceted and unique universities are. Scenarios—a common tool in foresight—would not be sufficient on their own to understand the possible futures of universities. Therefore, we first categorised universities into 10 different dimensions, such as societal purpose, international orientation, and educational organization, and identified different directions for development for each dimension. This allowed us to create a multidimensional description of possible development paths for universities, yielding in total 30 different paths and their combinations. The reality is somewhere between the idealized end-points.
In addition to helping understand various possible futures, the analysis where several dimensions and their paths are explained also provides a tool for the university units to examine their own position in relation to these possible developments. University units can differ significantly from one another, and no analytical tool that accounts for these differences can be sufficient. Our report offers such a tool by enabling discussion – with agreements and disagreements – of different development trajectories from the perspectives of diverse traditions and practices that can be found within any university.
Possibilities and Desirability – The Delphi Study
It was not only important to understand the possible futures universities may face. Equally crucial at the University of Turku was to understand what university members – researchers, students, administration, and other staff – think about these futures. To achieve such understanding, we conducted a Delphi study to ask what university members consider probable and desirable when it comes to the future. The statements were designed to provoke thoughts and bring out views that might not emerge in more traditional discussions. In addition to the probability and desirability assessments, we gathered valuable insights from the open comment sections, which often reveal perspectives that might be overlooked in the literature review.
Some Key Results
While the most interesting results cannot all be included in this text, some should be highlighted to provide a sense of the nature of the study.
First, universities are continuously balancing societal impact, economic goals, and fundamental research. The demands from the side of the wider society often pull in different directions. The Delphi study showed that working towards a societal mission is seen as desirable, but market orientation is expected to be more likely. A common thought and worry seems to be that universities are likely to shift towards more commercial interests, despite the tension this creates with their social responsibilities not measurable in economic terms.
Second, global research collaboration and local relevance create a significant tension. Universities aim to be part of global networks, while also expected to contribute to their local communities. The Delphi study revealed varying opinions on this balance. Some see global engagement as essential, while others stress the importance of local ties. Whether a university can succeed in both areas or must focus on one is a central question. The geopolitical tensions and the regional clusters this might create adds another path that might make the question between local and global even more difficult and multidimensional.
Third, in teaching, the main tension seems to lie between scalable, mass-oriented education and more personalised, tailored teaching. Scalable teaching allows universities to reach more students, but the Delphi study showed that personalized methods are considered more desirable. Yet, the study also indicated that standardised models are, according to the members of the university, more likely to prevail due to the scarcity of resources. Technology and its development will be an integral part of both scalable and personalised teaching paths (and everything in between) but different technological solutions might be associated with different paths.
Significance for the University Sector
The project and the report highlight the value of combining an analysis of the university operating environment and a more detailed study of the views of the university community. On the one hand, an analysis of the environment and the paths therein provides a tool to navigate the prospects and risks. On the other hand, the analysis of the members’ perspective helps the university understand where we stand now and what are the paths that the members recognise. Together, these two provide a robust view on the strategic status and importance of different possible trajectories for universities’ operating environment.
The research has broad applicability across universities worldwide. Through its dimensions and models, any higher education institution can map out and discuss likely trajectories, desired directions, and concerning paths ahead - regardless of their unique features. By combining extensive research literature with a Delphi study, the report opens a window into the possible futures of universities – or rather a map that can be used to navigate the long-term issues that these long-standing institutions face.
References
Virmajoki, V., Ahokas, I., Witoon, S., Ahlqvist, T., Kirveennummi, A., & Suomalainen, K.-M. (2024). Future directions and possibilities for the university: Report on literature review and Delphi study. A Report by University of Turku Strategic Planning Unit in collaboration with the Finland Futures Research Centre (FFRC). ISBN 978-952-249-617-1.